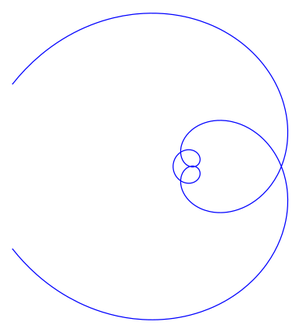
Galilean spiral
From Encyclopedia of Mathematics
A plane curve whose equation in polar coordinates is
$$\rho=a\phi^2-l,\quad l\geq0.$$
The spiral is symmetric with respect to the polar axis (see Fig.) and has a double point at the pole with tangents forming angles equal to $\pm\sqrt{l/a}$ with the polar axis.
The polar axis of a Galilean spiral contains infinitely many double points, for which $\rho=ak^2\pi^2-l$, where $k=1,2,\ldots$. The Galilean spiral is a so-called algebraic spiral (cf. Spirals). Named after G. Galilei (1683) in connection with his studies on the free fall of solids.
References
- [1] A.A. Savelov, "Planar curves", Moscow (1960) (In Russian)
How to Cite This Entry:
Galilean spiral. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Galilean_spiral&oldid=32536
Galilean spiral. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Galilean_spiral&oldid=32536
This article was adapted from an original article by D.D. Sokolov (originator), which appeared in Encyclopedia of Mathematics - ISBN 1402006098. See original article