Difference between revisions of "Fermat spiral"
From Encyclopedia of Mathematics
(TeX) |
(svg picture) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
They were first studied by P. Fermat (1636). | They were first studied by P. Fermat (1636). | ||
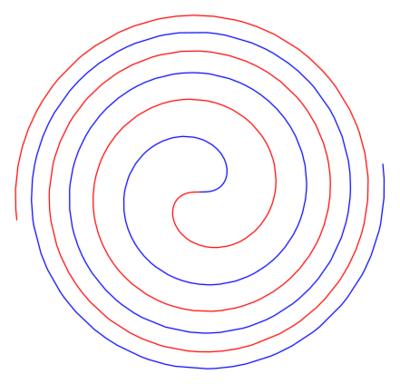
| − | + | [[File:Fermat spiral.svg|center|400px|Fermat spiral]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
====References==== | ====References==== | ||
| − | + | * {{Ref|1}} A.A. Savelov, "Planar curves" , Moscow (1960) (In Russian) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====References==== | ====References==== | ||
<table><TR><TD valign="top">[a1]</TD> <TD valign="top"> J.D. Lawrence, "A catalog of special plane curves" , Dover, reprint (1972)</TD></TR></table> | <table><TR><TD valign="top">[a1]</TD> <TD valign="top"> J.D. Lawrence, "A catalog of special plane curves" , Dover, reprint (1972)</TD></TR></table> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:35, 16 March 2023
A planar transcendental curve the equation of which in polar coordinates has the form
$$\rho=a\sqrt\phi.$$
To each value of $\phi$ correspond two values of $\rho$ — a positive and a negative one. The Fermat spiral is centrally symmetric relative to the pole, which is a point of inflection. It belongs to the class of so-called algebraic spirals.
They were first studied by P. Fermat (1636).
References
- [1] A.A. Savelov, "Planar curves" , Moscow (1960) (In Russian)
References
| [a1] | J.D. Lawrence, "A catalog of special plane curves" , Dover, reprint (1972) |
How to Cite This Entry:
Fermat spiral. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Fermat_spiral&oldid=52724
Fermat spiral. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Fermat_spiral&oldid=52724
This article was adapted from an original article by D.D. Sokolov (originator), which appeared in Encyclopedia of Mathematics - ISBN 1402006098. See original article