Difference between revisions of "Kolmogorov test"
(asy code to subpage) |
Ulf Rehmann (talk | contribs) m (tex encoded by computer) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | k0557601.png | ||
| + | $#A+1 = 55 n = 0 | ||
| + | $#C+1 = 55 : ~/encyclopedia/old_files/data/K055/K.0505760 Kolmogorov test | ||
| + | Automatically converted into TeX, above some diagnostics. | ||
| + | Please remove this comment and the {{TEX|auto}} line below, | ||
| + | if TeX found to be correct. | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{TEX|auto}} | ||
| + | {{TEX|done}} | ||
| + | |||
{{MSC|62G10}} | {{MSC|62G10}} | ||
[[Category:Nonparametric inference]] | [[Category:Nonparametric inference]] | ||
| − | A [[Statistical test|statistical test]] used for testing a simple non-parametric hypothesis | + | A [[Statistical test|statistical test]] used for testing a simple non-parametric hypothesis $ H _ {0} $, |
| + | according to which independent identically-distributed random variables $ X _ {1} \dots X _ {n} $ | ||
| + | have a given distribution function $ F $, | ||
| + | where the alternative hypothesis $ H _ {1} $ | ||
| + | is taken to be two-sided: | ||
| − | + | $$ | |
| + | | {\mathsf E} F _ {n} ( x) - F ( x) | > 0 , | ||
| + | $$ | ||
| − | where | + | where $ {\mathsf E} F _ {n} $ |
| + | is the [[Mathematical expectation|mathematical expectation]] of the empirical distribution function $ F _ {n} $. | ||
| + | The critical set of the Kolmogorov test is expressed by the inequality | ||
| − | + | $$ | |
| + | D _ {n} = \ | ||
| + | \sup _ | ||
| + | {| x | < \infty } \ | ||
| + | | F _ {n} ( x) - F ( x) | > \lambda _ {n} $$ | ||
| − | and is based on the following theorem, proved by A.N. Kolmogorov in 1933: If the hypothesis | + | and is based on the following theorem, proved by A.N. Kolmogorov in 1933: If the hypothesis $ H _ {0} $ |
| + | is true, then the distribution of the statistic $ D _ {n} $ | ||
| + | does not depend on $ F $; | ||
| + | also, as $ n \rightarrow \infty $, | ||
| − | < | + | $$ |
| + | {\mathsf P} | ||
| + | \{ \sqrt n D _ {n} < \lambda \} \rightarrow K ( \lambda ) ,\ \ | ||
| + | \lambda > 0 , | ||
| + | $$ | ||
where | where | ||
| − | + | $$ | |
| + | K ( \lambda ) = \ | ||
| + | \sum _ {m = - \infty } ^ \infty | ||
| + | ( - 1 ) ^ {m} e ^ {- 2 m ^ {2} \lambda ^ {2} } . | ||
| + | $$ | ||
| − | In 1948 N.V. Smirnov {{Cite|BS}} tabulated the Kolmogorov distribution function | + | In 1948 N.V. Smirnov {{Cite|BS}} tabulated the Kolmogorov distribution function $ K ( \lambda ) $. |
| + | According to the Kolmogorov test with significance level $ \alpha $, | ||
| + | $ 0 < \alpha < 0.5 $, | ||
| + | the hypothesis $ H _ {0} $ | ||
| + | must be rejected if $ D _ {n} \geq \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) $, | ||
| + | where $ \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) $ | ||
| + | is the critical value of the Kolmogorov test corresponding to the given significance level $ \alpha $ | ||
| + | and is the root of the equation $ {\mathsf P} \{ D _ {n} \geq \lambda \} = \alpha $. | ||
| − | To determine | + | To determine $ \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) $ |
| + | one recommends the use of the approximation of the limiting law of the Kolmogorov statistic $ D _ {n} $ | ||
| + | and its limiting distribution; see {{Cite|B}}, where it is shown that, as $ n \rightarrow \infty $ | ||
| + | and $ 0 < \lambda _ {0} < \lambda = O ( n ^ {1/3} ) $, | ||
| − | + | $$ \tag{* } | |
| + | {\mathsf P} | ||
| + | \left \{ | ||
| − | + | \frac{1}{18n} | |
| + | |||
| + | ( 6 n D _ {n} + 1 ) ^ {2} | ||
| + | \geq \lambda \right \} = | ||
| + | $$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | $$ | ||
| + | = \ | ||
| + | \left [ 1 - K \left ( \sqrt { | ||
| + | \frac \lambda {2} | ||
| + | } \right ) \right | ||
| + | ] \left [ 1 + O \left ( | ||
| + | \frac{1}{n} | ||
| + | \right ) \right ] . | ||
| + | $$ | ||
The application of the approximation (*) gives the following approximation of the critical value: | The application of the approximation (*) gives the following approximation of the critical value: | ||
| − | + | $$ | |
| + | \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) \approx \ | ||
| + | \sqrt { | ||
| + | \frac{z}{2n} | ||
| + | } - | ||
| + | \frac{1}{6n} | ||
| + | , | ||
| + | $$ | ||
| − | where | + | where $ z $ |
| + | is the root of the equation $ 1 - K ( \sqrt {z/2 } ) = \alpha $. | ||
| − | In practice, for the calculation of the value of the statistic | + | In practice, for the calculation of the value of the statistic $ D _ {n} $ |
| + | one uses the fact that | ||
| − | + | $$ | |
| + | D _ {n} = \ | ||
| + | \max ( D _ {n} ^ {+} , D _ {n} ^ {-} ) , | ||
| + | $$ | ||
where | where | ||
| − | + | $$ | |
| + | D _ {n} ^ {+} = \ | ||
| + | \max _ {1 \leq m \leq n } \ | ||
| + | \left ( | ||
| + | |||
| + | \frac{m}{n} | ||
| + | - F | ||
| + | ( X _ {(} m) ) | ||
| + | \right ) , | ||
| + | $$ | ||
| − | + | $$ | |
| + | D _ {n} ^ {-} = \max _ {1 \leq m \leq n } | ||
| + | \left ( F ( X _ {(} m) ) - m- | ||
| + | \frac{1}{n} | ||
| + | \right ) , | ||
| + | $$ | ||
| − | and | + | and $ X _ {(} 1) \leq \dots \leq X _ {(} n) $ |
| + | is the [[Variational series|variational series]] (or set of order statistics) constructed from the sample $ X _ {1} \dots X _ {n} $. | ||
| + | The Kolmogorov test has the following geometric interpretation (see Fig.). | ||
{{:Kolmogorov test/Fig1}} | {{:Kolmogorov test/Fig1}} | ||
| − | The graph of the functions | + | The graph of the functions $ F _ {n} ( x) $, |
| + | $ F _ {n} ( x) \pm \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) $ | ||
| + | is depicted in the $ xy $- | ||
| + | plane. The shaded region is the confidence zone at level $ 1 - \alpha $ | ||
| + | for the distribution function $ F $, | ||
| + | since if the hypothesis $ H _ {0} $ | ||
| + | is true, then according to Kolmogorov's theorem | ||
| − | < | + | $$ |
| + | {\mathsf P} \{ F _ {n} ( x) - \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) < F ( x) < F _ {n} ( x) + \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) \} | ||
| + | \approx 1 - \alpha . | ||
| + | $$ | ||
| − | If the graph of | + | If the graph of $ F $ |
| + | does not leave the shaded region then, according to the Kolmogorov test, $ H _ {0} $ | ||
| + | must be accepted with significance level $ \alpha $; | ||
| + | otherwise $ H _ {0} $ | ||
| + | is rejected. | ||
The Kolmogorov test gave a strong impetus to the development of mathematical statistics, being the start of much research on new methods of statistical analysis lying at the foundations of non-parametric statistics. | The Kolmogorov test gave a strong impetus to the development of mathematical statistics, being the start of much research on new methods of statistical analysis lying at the foundations of non-parametric statistics. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 169: | ||
====Comments==== | ====Comments==== | ||
| − | Tests based on | + | Tests based on $ D _ {n} $ |
| + | and $ \widetilde{D} _ {n} = \sup _ {x} ( F _ {n} ( x) - F ( x)) $, | ||
| + | and similar tests for a two-sample problem based on $ D _ {m,n} = \sup _ {x} | F _ {m} ( x) - G _ {n} ( x) | $ | ||
| + | and $ \widetilde{D} _ {m,n} = \sup _ {x} ( F _ {m} ( x) - G _ {n} ( x)) $, | ||
| + | where $ G _ {m} $ | ||
| + | is the empirical distribution function for samples of size $ m $ | ||
| + | for a population with distribution function $ G $, | ||
| + | are also called Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests, cf. also [[Kolmogorov–Smirnov test|Kolmogorov–Smirnov test]]. | ||
====References==== | ====References==== | ||
Latest revision as of 22:14, 5 June 2020
2020 Mathematics Subject Classification: Primary: 62G10 [MSN][ZBL]
A statistical test used for testing a simple non-parametric hypothesis $ H _ {0} $, according to which independent identically-distributed random variables $ X _ {1} \dots X _ {n} $ have a given distribution function $ F $, where the alternative hypothesis $ H _ {1} $ is taken to be two-sided:
$$ | {\mathsf E} F _ {n} ( x) - F ( x) | > 0 , $$
where $ {\mathsf E} F _ {n} $ is the mathematical expectation of the empirical distribution function $ F _ {n} $. The critical set of the Kolmogorov test is expressed by the inequality
$$ D _ {n} = \ \sup _ {| x | < \infty } \ | F _ {n} ( x) - F ( x) | > \lambda _ {n} $$
and is based on the following theorem, proved by A.N. Kolmogorov in 1933: If the hypothesis $ H _ {0} $ is true, then the distribution of the statistic $ D _ {n} $ does not depend on $ F $; also, as $ n \rightarrow \infty $,
$$ {\mathsf P} \{ \sqrt n D _ {n} < \lambda \} \rightarrow K ( \lambda ) ,\ \ \lambda > 0 , $$
where
$$ K ( \lambda ) = \ \sum _ {m = - \infty } ^ \infty ( - 1 ) ^ {m} e ^ {- 2 m ^ {2} \lambda ^ {2} } . $$
In 1948 N.V. Smirnov [BS] tabulated the Kolmogorov distribution function $ K ( \lambda ) $. According to the Kolmogorov test with significance level $ \alpha $, $ 0 < \alpha < 0.5 $, the hypothesis $ H _ {0} $ must be rejected if $ D _ {n} \geq \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) $, where $ \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) $ is the critical value of the Kolmogorov test corresponding to the given significance level $ \alpha $ and is the root of the equation $ {\mathsf P} \{ D _ {n} \geq \lambda \} = \alpha $.
To determine $ \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) $ one recommends the use of the approximation of the limiting law of the Kolmogorov statistic $ D _ {n} $ and its limiting distribution; see [B], where it is shown that, as $ n \rightarrow \infty $ and $ 0 < \lambda _ {0} < \lambda = O ( n ^ {1/3} ) $,
$$ \tag{* } {\mathsf P} \left \{ \frac{1}{18n} ( 6 n D _ {n} + 1 ) ^ {2} \geq \lambda \right \} = $$
$$ = \ \left [ 1 - K \left ( \sqrt { \frac \lambda {2} } \right ) \right ] \left [ 1 + O \left ( \frac{1}{n} \right ) \right ] . $$
The application of the approximation (*) gives the following approximation of the critical value:
$$ \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) \approx \ \sqrt { \frac{z}{2n} } - \frac{1}{6n} , $$
where $ z $ is the root of the equation $ 1 - K ( \sqrt {z/2 } ) = \alpha $.
In practice, for the calculation of the value of the statistic $ D _ {n} $ one uses the fact that
$$ D _ {n} = \ \max ( D _ {n} ^ {+} , D _ {n} ^ {-} ) , $$
where
$$ D _ {n} ^ {+} = \ \max _ {1 \leq m \leq n } \ \left ( \frac{m}{n} - F ( X _ {(} m) ) \right ) , $$
$$ D _ {n} ^ {-} = \max _ {1 \leq m \leq n } \left ( F ( X _ {(} m) ) - m- \frac{1}{n} \right ) , $$
and $ X _ {(} 1) \leq \dots \leq X _ {(} n) $ is the variational series (or set of order statistics) constructed from the sample $ X _ {1} \dots X _ {n} $. The Kolmogorov test has the following geometric interpretation (see Fig.).
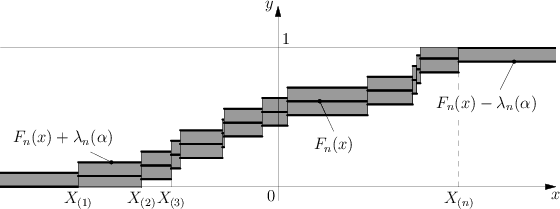
The graph of the functions $ F _ {n} ( x) $, $ F _ {n} ( x) \pm \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) $ is depicted in the $ xy $- plane. The shaded region is the confidence zone at level $ 1 - \alpha $ for the distribution function $ F $, since if the hypothesis $ H _ {0} $ is true, then according to Kolmogorov's theorem
$$ {\mathsf P} \{ F _ {n} ( x) - \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) < F ( x) < F _ {n} ( x) + \lambda _ {n} ( \alpha ) \} \approx 1 - \alpha . $$
If the graph of $ F $ does not leave the shaded region then, according to the Kolmogorov test, $ H _ {0} $ must be accepted with significance level $ \alpha $; otherwise $ H _ {0} $ is rejected.
The Kolmogorov test gave a strong impetus to the development of mathematical statistics, being the start of much research on new methods of statistical analysis lying at the foundations of non-parametric statistics.
References
| [K] | A.N. Kolmogorov, "Sulla determinizione empirica di una legge di distribuzione" Giorn. Ist. Ital. Attuari , 4 (1933) pp. 83–91 |
| [S] | N.V. Smirnov, "On estimating the discrepancy between empirical distribiution curves for two independent samples" Byull. Moskov. Gos. Univ. Ser. A , 2 : 2 (1938) pp. 3–14 (In Russian) |
| [B] | L.N. Bol'shev, "Asymptotically Pearson transformations" Theor. Probab. Appl. , 8 (1963) pp. 121–146 Teor. Veroyatnost. i Primenen. , 8 : 2 (1963) pp. 129–155 Zbl 0125.09103 |
| [BS] | L.N. Bol'shev, N.V. Smirnov, "Tables of mathematical statistics" , Libr. math. tables , 46 , Nauka (1983) (In Russian) (Processed by L.S. Bark and E.S. Kedrova) Zbl 0529.62099 |
Comments
Tests based on $ D _ {n} $ and $ \widetilde{D} _ {n} = \sup _ {x} ( F _ {n} ( x) - F ( x)) $, and similar tests for a two-sample problem based on $ D _ {m,n} = \sup _ {x} | F _ {m} ( x) - G _ {n} ( x) | $ and $ \widetilde{D} _ {m,n} = \sup _ {x} ( F _ {m} ( x) - G _ {n} ( x)) $, where $ G _ {m} $ is the empirical distribution function for samples of size $ m $ for a population with distribution function $ G $, are also called Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests, cf. also Kolmogorov–Smirnov test.
References
| [N] | G.E. Noether, "A brief survey of nonparametric statistics" R.V. Hogg (ed.) , Studies in statistics , Math. Assoc. Amer. (1978) pp. 3–65 Zbl 0413.62023 |
| [HW] | M. Hollander, D.A. Wolfe, "Nonparametric statistical methods" , Wiley (1973) MR0353556 Zbl 0277.62030 |
Kolmogorov test. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Kolmogorov_test&oldid=35616