Difference between revisions of "Tangent line"
m (header spacing) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
''to a curve'' | ''to a curve'' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{MSC|53|58}} | ||
| + | {{TEX|done}} | ||
| + | $\newcommand{\vect}[1]{\mathbf{#1}}$ | ||
<span id="Fig1"> | <span id="Fig1"> | ||
[[File:Tangent-line-1.png| right| frame| Figure 1. The tangent $MT$ (in red) to the line $L$ at the point $M$ ([[Media:Tangent-line-1.pdf|pdf]]) ]] | [[File:Tangent-line-1.png| right| frame| Figure 1. The tangent $MT$ (in red) to the line $L$ at the point $M$ ([[Media:Tangent-line-1.pdf|pdf]]) ]] | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
| − | + | The tangent line to a curve is | |
| + | a straight line representing the limiting position of the secants. Let $M$ be a point on a curve $L$ ([[#Fig1|Fig. 1]]). A second point $M_1$ is chosen on $L$ and the straight line $M_1$ is drawn. The point $M$ is regarded as fixed, and $M_1$ approaches $M$ along the curve $L$. If, as $M_1$ goes to $M$, the line $MM_1$ tends to a limiting line $MT$, then $MT$ is called the tangent to $L$ at $M$. | ||
<span id="Fig2"> | <span id="Fig2"> | ||
[[File:Tangent-line-2.png| right| frame| Figure 2. A curve $L$ and point $M$ on it without a tangent ([[Media:Tangent-line-2.pdf|pdf]]) ]] | [[File:Tangent-line-2.png| right| frame| Figure 2. A curve $L$ and point $M$ on it without a tangent ([[Media:Tangent-line-2.pdf|pdf]]) ]] | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
| − | Not every continuous curve has a tangent, since $MM_1$ need not tend to a limiting position at all, or it may tend to two distinct limiting positions as $M_1$ tends to $M$ from different sides of $L$ ([[#Fig2|Fig. 2]]). If a curve in the plane with rectangular coordinates is defined by the equation $y=f(x)$ and $f$ is differentiable at the point $x_0$, then the slope of the tangent at $M$ is equal to the value of the derivative $f^\prime(x_0)$ at $x_0$; the equation of the tangent at this point has the form | + | Not every continuous curve has a tangent, since $MM_1$ need not tend to a limiting position at all, or it may tend to two distinct limiting positions as $M_1$ tends to $M$ from different sides of $L$ ([[#Fig2|Fig. 2]]). |
| + | |||
| + | If a curve in the plane with rectangular coordinates is defined by the equation $y=f(x)$ and $f$ is differentiable at the point $x_0$, then the slope of the tangent at $M$ is equal to the value of the derivative $f^\prime(x_0)$ at $x_0$; the equation of the tangent at this point has the form | ||
$$ | $$ | ||
y - f(x_0) = f^\prime(x_0)(x - x_0). | y - f(x_0) = f^\prime(x_0)(x - x_0). | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |valign="top"|{{Ref|BeGo}}||valign="top"| M. Berger, B. Gostiaux, "Differential geometry: manifolds, curves, and surfaces", Springer (1988) (Translated from French) | + | |valign="top"|{{Ref|BeGo}}||valign="top"| M. Berger, B. Gostiaux, "Differential geometry: manifolds, curves, and surfaces", Springer (1988) (Translated from French) {{MR|0917479}} {{ZBL|0629.53001}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |valign="top"|{{Ref|Co}}||valign="top"| H.S.M. Coxeter, "Introduction to geometry", Wiley (1961) | + | |valign="top"|{{Ref|Co}}||valign="top"| H.S.M. Coxeter, "Introduction to geometry", Wiley (1961) {{MR|1531486}} {{MR|0123930}} {{ZBL|0095.34502}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |valign="top"|{{Ref|Gu}}||valign="top"| H.W. Guggenheimer, "Differential geometry", McGraw-Hill (1963) | + | |valign="top"|{{Ref|Gu}}||valign="top"| H.W. Guggenheimer, "Differential geometry", McGraw-Hill (1963) {{MR|0156266}} {{ZBL|0116.13402}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |valign="top"|{{Ref|HiCo}}||valign="top"| D. Hilbert, S.E. Cohn-Vossen, "Geometry and the imagination", Chelsea (1952) (Translated from German) | + | |valign="top"|{{Ref|HiCo}}||valign="top"| D. Hilbert, S.E. Cohn-Vossen, "Geometry and the imagination", Chelsea (1952) (Translated from German) {{MR|0046650}} {{ZBL|0047.38806}} |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:50, 25 April 2012
to a curve
2020 Mathematics Subject Classification: Primary: 53-XX Secondary: 58-XX [MSN][ZBL]
$\newcommand{\vect}[1]{\mathbf{#1}}$
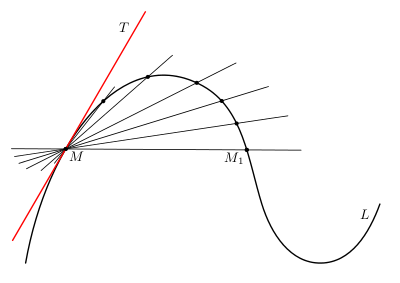
The tangent line to a curve is a straight line representing the limiting position of the secants. Let $M$ be a point on a curve $L$ (Fig. 1). A second point $M_1$ is chosen on $L$ and the straight line $M_1$ is drawn. The point $M$ is regarded as fixed, and $M_1$ approaches $M$ along the curve $L$. If, as $M_1$ goes to $M$, the line $MM_1$ tends to a limiting line $MT$, then $MT$ is called the tangent to $L$ at $M$.
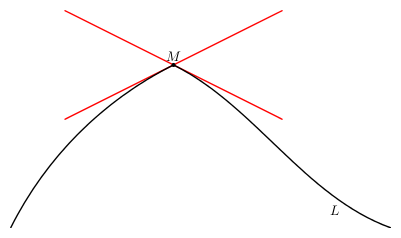
Not every continuous curve has a tangent, since $MM_1$ need not tend to a limiting position at all, or it may tend to two distinct limiting positions as $M_1$ tends to $M$ from different sides of $L$ (Fig. 2).
If a curve in the plane with rectangular coordinates is defined by the equation $y=f(x)$ and $f$ is differentiable at the point $x_0$, then the slope of the tangent at $M$ is equal to the value of the derivative $f^\prime(x_0)$ at $x_0$; the equation of the tangent at this point has the form $$ y - f(x_0) = f^\prime(x_0)(x - x_0). $$ The equation of the tangent to a curve $\vect{r} = \vect{r}(t)$ in space is $$ \vect{t}(\lambda) = \vect{r} + \lambda \frac{\mathrm{d}\vect{r}}{\mathrm{d}t}, \quad \lambda \in \R. $$
By a tangent to a surface $S$ at a point $M$ one means a straight line passing through $M$ and lying in the tangent plane to $S$ at $M$.
References
| [BeGo] | M. Berger, B. Gostiaux, "Differential geometry: manifolds, curves, and surfaces", Springer (1988) (Translated from French) MR0917479 Zbl 0629.53001 |
| [Co] | H.S.M. Coxeter, "Introduction to geometry", Wiley (1961) MR1531486 MR0123930 Zbl 0095.34502 |
| [Gu] | H.W. Guggenheimer, "Differential geometry", McGraw-Hill (1963) MR0156266 Zbl 0116.13402 |
| [HiCo] | D. Hilbert, S.E. Cohn-Vossen, "Geometry and the imagination", Chelsea (1952) (Translated from German) MR0046650 Zbl 0047.38806 |
Tangent line. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Tangent_line&oldid=25291