Difference between revisions of "User:Boris Tsirelson/sandbox1"
From Encyclopedia of Mathematics
| (292 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <ref> [http://hea-www.harvard.edu/AstroStat http://hea-www.harvard.edu/AstroStat]; <nowiki> http://www.incagroup.org </nowiki>; <nowiki> http://astrostatistics.psu.edu </nowiki> </ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ====Notes==== | |
| − | + | <references /> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ------------------------------------------- | ||
| − | |||
{| | {| | ||
| − | | | + | | A || B || C |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | X || Y || Z |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ----------------------------------------- | ||
| + | ----------------------------------------- | ||
| + | |||
| + | $\newcommand*{\longhookrightarrow}{\lhook\joinrel\relbar\joinrel\rightarrow}$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(100,100); | ||
| + | label(scale(1.7)*'$T(\\Sigma)\hookrightarrow T(\\Sigma,X)$',(0,0)); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | size(220,220); | ||
| + | |||
| + | import math; | ||
| + | |||
| + | int kmax=40; | ||
| + | |||
| + | guide g; | ||
| + | for (int k=-kmax; k<=kmax; ++k) { | ||
| + | real phi = 0.2*k*pi; | ||
| + | real rho = 1; | ||
| + | if (k!=0) { | ||
| + | rho = sin(phi)/phi; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | pair z=rho*expi(phi); | ||
| + | g=g..z; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | draw (g); | ||
| + | |||
| + | defaultpen(0.75); | ||
| + | draw ( (0,0)--(1.3,0), dotted, Arrow(SimpleHead,5) ); | ||
| + | dot ( (1,0) ); | ||
| + | label ( "$a$", (1,0), NE ); | ||
| + | |||
| + | </asy> | ||
Latest revision as of 07:12, 13 March 2016
Notes
- ↑ http://hea-www.harvard.edu/AstroStat; http://www.incagroup.org ; http://astrostatistics.psu.edu
| A | B | C |
| X | Y | Z |
$\newcommand*{\longhookrightarrow}{\lhook\joinrel\relbar\joinrel\rightarrow}$
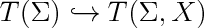

How to Cite This Entry:
Boris Tsirelson/sandbox1. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Boris_Tsirelson/sandbox1&oldid=21103
Boris Tsirelson/sandbox1. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Boris_Tsirelson/sandbox1&oldid=21103